How To Find Resultant Force On A Beam
Sum all the x and y components of the forces to find FRA. The bending moment at a given section of a beam is defined as the resultant moment about that section of either all the forces to the left of the section or of all the forces to the right of the section.

Calculating Resultant Forces Vector Diagrams Graphs Work Done Calculations Equilibrium Parallelogram Of Forces Tension Vector Forces Gcse 9 1 Physics Igcse Revision Notes
P-238 supports a load which varies an intensity of 220 Nm to 890 Nm.

How to find resultant force on a beam. The shearing force of all the forces acting on the segment of the beam to the left of the section as shown in Figure 45e is determined as follows. To determine the reactions at supports follow these simple steps. The equivalent resultant force and couple moment acting at A and then the equivalent single force location along the beam AB.
Length of beam m ft Force F1 N lb f distance from R 1 m ft Force F2 N lb f distance from R 1 m ft. When a beam is simply supported at each end all the downward forces are balanced by equal and opposite upward forces and the beam is said to be held in Equilibrium ie. To give this moment the resultant force must be a distance of 475150 32 m from A.
These consist of a summation of forces in the vertical direction and a summation of moments. As shown in Fig. Experiments show that when an object.
Determine the resultant force and specify where itacts on the beam measured from A. The calculator below can be used to calculate the support forces - R 1 and R 2 - for beams with up to 6 asymmetrically loads. This is just a few minutes of a complete course.
Online Beam Support Force Calculator. Get full lessons more subjects at. The negative sign indicates a negative shearing force which was established from the sign convention for a shearing force.
We draw a parallelogram to help us find the resultant force. Calculate the magnitude and position of the resultant load. 230 b the support roller at B exerts a normal force on the beam at its point of contact.
Find and sum all the moments resulting from moving each force to A. The line of action of this force is defined by the 3-4-5 triangle. The obtained expression is valid for the entire beam.
The resultant force is the vector sum between the components. If there are several forces acting on the same point we can apply the polygon rule to find their resultant. 1 a the bending moment is either Mx or Mx.
This is because the beam is static and therefore not rotating. The force x. Figure 1-30 shows a beam under transverse loading.
134 Introduction to Reaction Forces and Moments on Beams Under Transverse Loading. Similarly the bending moment at any section of a beam may be found by adding the moments from the left or from the right of the section considered. For example if a box of 15 kg is subject to 5 forces which make it accelerate 20 ms 2 north-west then the resultant force is directed north-west and has the magnitude equal to 15 kg 20 ms 2 30 N.
The resultant force can be determined also for three-dimensional force systems by using the polygon rule. The total load exerted by the beams own weight plus any additional applied load are completely balanced by the sum of the two reactions at the two supports. This video shows how to find the resultant force of two vectors using the parallelogram method.
Two equations of equilibrium may be applied to find the reaction loads applied to such a beam by the supports. Problem 238 The beam AB in Fig. Often however we know the forces that act on an object and we need to find the resultant force.
The moments of the forces about A 100 15 150 25 200 35 475 Nm in a clockwise direction. Shift the FRAto a distance d such that d MRAFRy. The shear force at any section of a beam may be found by summing all the vertical forces to the left or to the right of the section under consideration.
Let the sum of moments about a reaction point equal to ZERO M 0 All we need to know about moments at this stage is that they are equal to the force multiplied by the distance from a point ie. The resultant force 100 150 200 150 N in a downward direction.

Determine The Magnitude And Direction Of The Resultant Force Youtube

Finding The Resultant Force Using Funicular Construction For Forces F I Download Scientific Diagram

Determine The Resultant Force And Specify Where It Acts On The Beam Youtube

Determine The Resultant Force And Specify Where It Acts On The Beam Youtube

Determine The Resultant Force And Specify Where It Acts On The Beam Youtube
Strategy Interpreting Beam Resultant Forces And Moments

Resultant Force An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
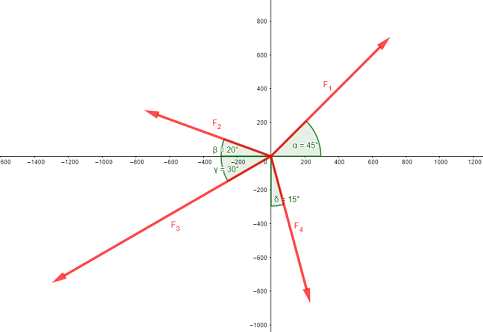
Calculation Of The Resultant Force Mechanics Exercise And Solution
A System Of Loads Acting On A Beam Is Shown In Fig Determine The Resultant Of The Loads Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

Find Location Of Resultant Of Forces Without Using Moments Engineering Stack Exchange

Determine The Length B Of The Triangular Load And Its Position A On The Beam Such That The Equivalent Resultant Force Is Zero And The Resultant Couple Moment Is 8 Kn

Pin By Rajan On Beam Reaction System Force How To Find Out

Determine The Resultant Force And Specify Where It Acts On The Beam Youtube

Direction Of The Resultant Force In Hinge Supports Engineering Stack Exchange

Resultant Moment And Shear Force At The Maximum Impact Force Download Scientific Diagram
Strategy Interpreting Beam Resultant Forces And Moments
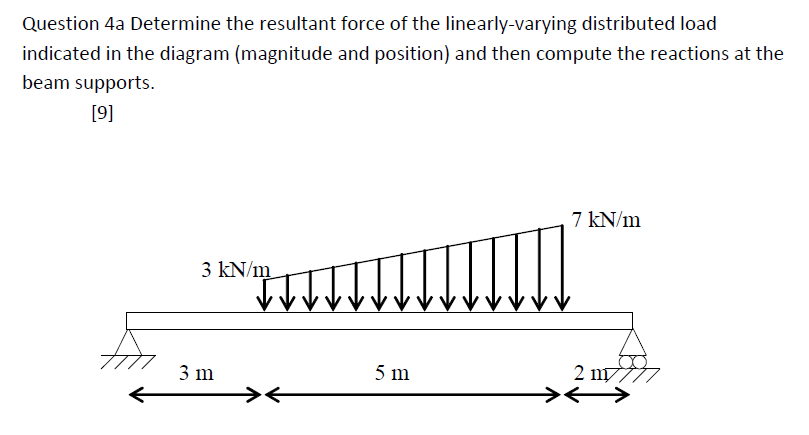
Determine The Resultant Force Of The Linearly Varying Chegg Com
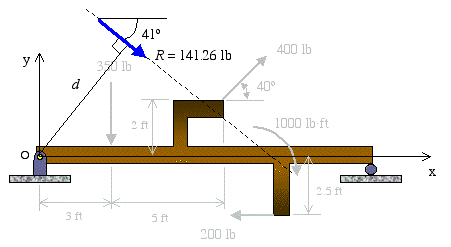

Posting Komentar untuk "How To Find Resultant Force On A Beam"