Resultant Force On A Beam
Beam resultants are required for many beam post-processing operations such as calculating complete stress results and displaying results on beam sections. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.

Determine The Resultant Force And Specify Where It Acts On The Beam Youtube
If the resultant force working on the roof beam of the shallow mined-out areas is considered as that on the centroid of the roof beam then the resultant force F can be derived from Eq.

Resultant force on a beam. In the cut section the resultant forces F y and moment couple M z act to maintain equilibrium. Beam equations for Resultant Forces Shear Forces Bending Moments and Deflection can be found for each beam case shown. By convention the Shearing Force on the left of the beam would be rotated clockwise by the combined actions of R1 and W and is therefore labelled positive.
These consist of a summation of forces in the vertical direction and a summation of moments. In beam a Fy is negative while in beam b F y is positive. Often however we know the forces that act on an object and we need.
The diagram below shows how the applied force is in the downward direction and the resultant internal forces. Determine the resultant couple moment acting onthe beam. At the beams free end the shear force is zero.
This resultant internal force keeps the beambody in equilibrium ie applied force on beam is equal to the internal shear forces in the beam. If you require less simply leave them blank. Assume b 3 m.
The resultant force is the vector sum between the components. Geometry Method The magnitude of the resultant force is equivalent to the area under the curve of the distributed load 10 kNm 1 m 3 m 2 m. Its the sum of all forces and their directions.
Determine the resultant force and specify where itacts on the beam measured from A. At the wall of a cantilever beam the shear force equals the vertical reaction at the wall. Beam Resultant Forces Component Index Karamba3D 6Results Beam Resultant Forces Retrieves maximum resultant section forces for all beam elements of the model.
Since the beam is in Equilibrium the Shearing Forces must each start and finish on the same line. GO TO NEW INTERFACE FRAMETRUSS. The resultant force can be determined also for three-dimensional force systems by using the polygon rule.
To predict the behavior of structures the magnitudes of these forces must be known. Beam Calculator Online Calculate the reactions Draws Bending Moment Shear Force Axial Force We updated the beam calculator interface and added additional features for calculating beams calculation of statically indeterminate beams image saving and section selection. For example if a box of 15 kg is subject to 5 forces which make it accelerate 20 ms 2 north-west then the resultant force is directed north-west and has the magnitude equal to 15 kg 20 ms 2 30 N.
Beam resultants are derived from element forces. Simply select the picture which most resembles the beam configuration and loading condition you are interested in for a detailed summary of all the structural properties. Which indicates that the resultant force R has the same direction as a and has magnitude equal to the product m a.
647F U X 4a 1X 3 2b 1X c 1 The motion equation of the roof beam is described by F MX. Two equations of equilibrium may be applied to find the reaction loads applied to such a beam by the supports. M z is negative in both the beams.
To ensure that beam resultants are included in your results file be sure to include a force output request in your solution. The right hand Shearing Force is. GO TO NEW INTERFACE BEAM.
A resultant force is also known as the net force acting on an object. The calculator above can solve for up to 5 different forces and angles. Structure always reports values for the resultant forces and moments for the positive direction of the free body diagram.
Part A Determine the magnitude of the resultant force. If there are several forces acting on the same point we can apply the polygon rule to find their resultant. Beam Design Formulas.
When a beam or frame is subjected to transverse loadings the three possible internal forces that are developed are the normal or axial force the shearing force and the bending moment as shown in section k of the cantilever of Figure 41. Determine the resultant force and specify where it acts on the beam measured from A Figure 1. On any beam segment where no loads are applied the shear force remains constant horizontal line.
The Resultant Of Two Forces Solutions Examples Videos Worksheets Games Activities

Chapter 3 Shearing Force And Bending Moment Diagrams Summary Bending Moment Shear Force In This Moment

2 53 Resultant Force Example 3 Youtube

Determine The Resultant Force And Specify Where It Acts On The Beam Youtube

Direction Of The Resultant Force In Hinge Supports Engineering Stack Exchange

Determine The Resultant Force And Specify Where It Acts On The Beam Youtube
Strategy Interpreting Beam Resultant Forces And Moments

Pin By Rajan On Beam Reaction System Force How To Find Out

Magnitude And Angle Of The Resultant Force Kristakingmath Youtube

Determine The Resultant Force And Specify Where It Acts On The Beam Youtube

Coplanar Concurrent Forces Xvi Position Of The Resultant Force Positivity Force Mechanic

Calculating Resultant Forces Vector Diagrams Graphs Work Done Calculations Equilibrium Parallelogram Of Forces Tension Vector Forces Gcse 9 1 Physics Igcse Revision Notes

Making Of Stirrups For Beam Beams Structural Engineering Stirrups

How To Resolve The Issues For Calculating The Design Moment Strength Of A Doubly Rc Section Concrete Design Beams In This Moment

Resultant Force An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Determine The Resultant Force And Specify Where It Acts On The Beam Youtube

Determine The Magnitude And Direction Of The Resultant Force Youtube

Bending Moment And Shear Force Computation Bending Moment Shear Force In This Moment
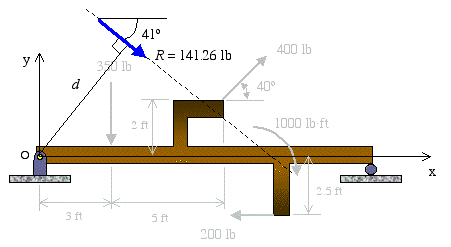
Posting Komentar untuk "Resultant Force On A Beam"